
Akal Homoeo Care Centre
Spl.in: All Critical & Chronic, Disease (Cancer, Diabtic, Arthrist)

Spl.in: All Critical & Chronic, Disease (Cancer, Diabtic, Arthrist)
Hepatitis A is a viral infection caused by the Hepatitis A virus. Many people in India call this disease ‘Jaundice’. Infections with Hepatitis A virus are mild in majority cases, with most people making a full recovery. In rare instances, a person with a compromised immunity may develop severe and life-threatening complications.
Hepatitis A virus is transmitted through food or water contaminated with feces of infected persons. You have higher chances of getting infected with the disease if you are in close contact with a person who is carrying the virus, even if he has no signs or symptoms.
After being exposed to the virus, it takes around 2 to 7 weeks to develop signs and symptoms of Hepatitis A. Symptoms usually last for about 2 months but may last longer in some cases.
Symptoms and signs that you may suffer from are:
After some days, you may develop certain symptoms that indicate the liver is affected, such as:
You’re at increased risk of hepatitis A if you are:
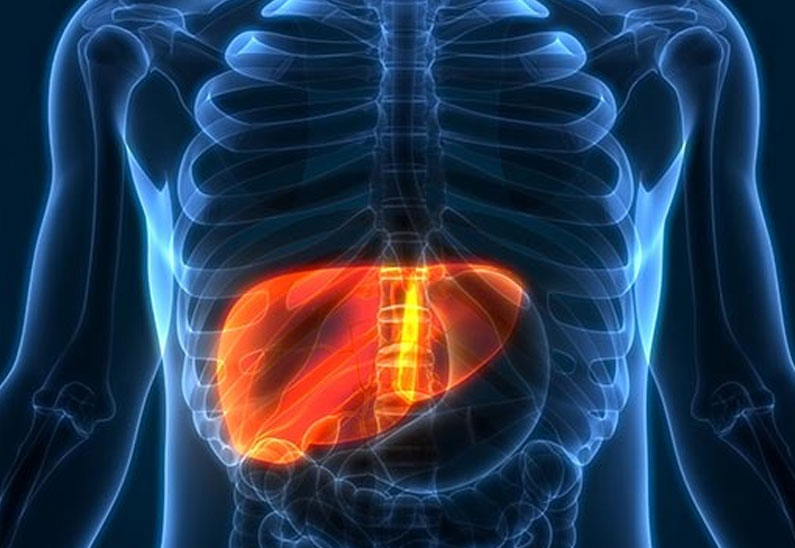
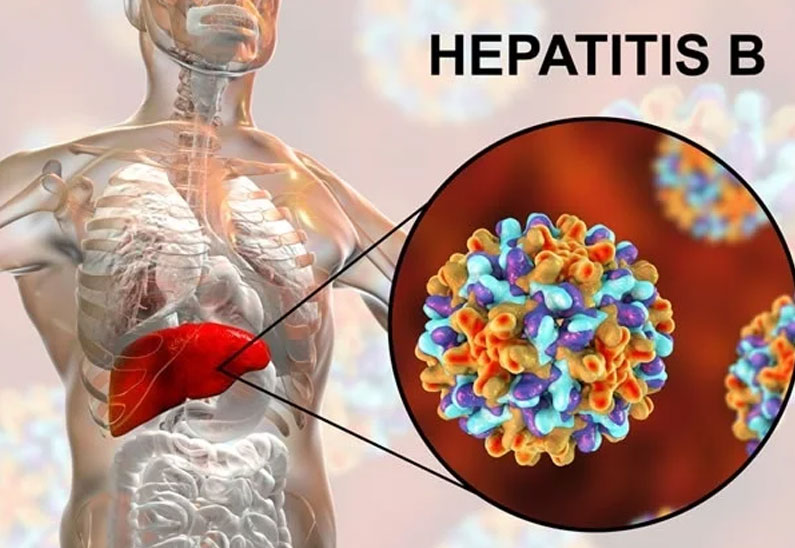
Hepatitis B is a viral infection caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV). This virus is capable of causing life-long infection, liver cirrhosis (scaring), liver failure, liver cancer and death.
As mentioned above the cause of Hepatitis B is the virus- HBV. The virus spreads when blood from an infected person enters the body of a non-infected person. This virus enters the blood stream and reaches the liver where it reproduces and releases large numbers of new viruses into the bloodstream. HBV can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and can still be capable of causing infection. HBV is mainly found in the blood of infected individuals. Saliva, semen, vaginal secretions and breast milk also contain the virus but in lower concentrations as compared to the blood. Feces, nasal secretions, sputum, sweat, tears, urine and vomit have not been implicated in the spread of Hepatitis B. Unless they are visibly contaminated with blood, the risk of contracting hepatitis B from these fluids is practically nonexistent. Hepatitis B is not transmitted by casual contact, hugging, by sharing eating utensils, through food or water, etc. After a person has been exposed to the HBV, the blood test (HBsAg) will become positive on an average within 4 weeks (range 1- 9 weeks). Usually within 15 weeks of onset of the symptoms, this test becomes negative in most individuals (except those who have developed chronic infection).
Sometimes a person with HBV infection may not have any symptoms at all. In patients who do develop symptoms, they occur on an average of about 12 weeks (range 9-21 weeks) after exposure to hepatitis B virus. About 70% of the patients develop symptoms of Hepatitis B.
Almost one in every 70 persons in the US, that is 1.45% of the American population is estimated to be suffering with Hep C. The same is true with India and many other countries. Hepatitis means an inflammation of the liver. When the inflammation of the liver is due to a specific RNA virus which leads to chronic inflammation, it is called Hepatitis C. There are several virus names as A,B,C,D,E, etc. which are known to affect the liver, producing Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, etc. In fact, this particular virus has a capacity to induce not only inflammation but scarring of the liver, which is called as cirrhosis of liver. The virus tends to multiply rapidly hence not allowing to develop natural antibodies in adequate quantity. This virus is a slow and silent destroyer of liver cell. It may so happen that one may not realize the infection for years together. After a prolonged state of inflammation cirrhosis may take place, which may take ten to fifty years. It is a very slow process, if not aggravated by certain food habits and alcohol.
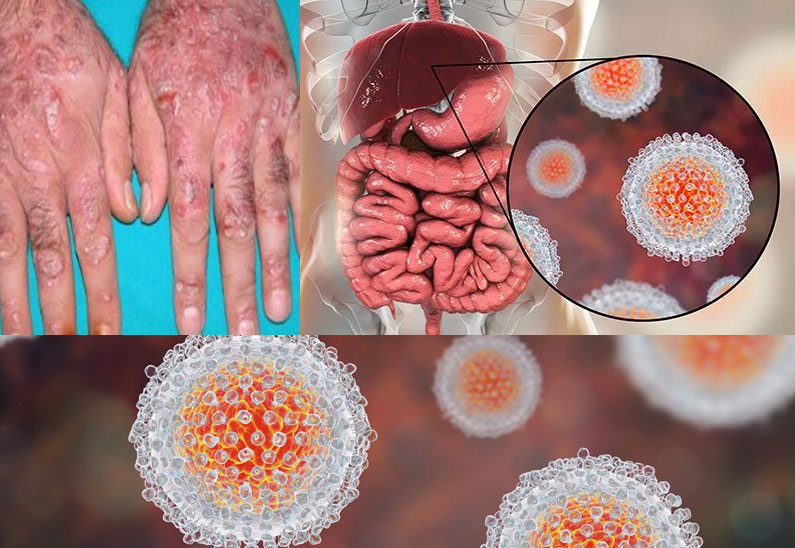
The HCV infection takes years to produce symptoms in those infected with this virus. About 35% of the infected people may produce symptoms while the rest may not produce symptoms at all. Hepatitis C does not have prominent symptoms in the early stage. The infected individual may experience vague symptoms such as abdominal pain, impaired digestion, loss of appetite, lassitude, weakness, itching, etc. However, these symptoms are so common that it is hard to point towards the diagnosis of Hepatitis C. The severity of the symptoms is not directly proportional to the intensity of liver dysfunction, however. Patients in the advanced stage may experience more severe symptoms such as yellow sclera, sometimes paleness (whiteness) of eyes, loss of appetite, depression, bleeding from rectum, bloody vomiting, exhaustion and weight loss. Advanced stage symptoms of Hepatitis C are those due to chronic inflammation of liver (hepatitis), cirrhosis (scarring of tissues) of liver and/or liver failure. The patients with acute Hepatitis C present with lethargic feeling, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, body pain, and exhaustion. Objectively, one may observe yellowness of sclera (icterus or jaundice as it is called).
Hepatitis C being a chronic infection, it has certain long term complications. About 80% or more patients tend to develop chronic symptoms due to recurring or chronic liver inflammation. Many of the HCV infected patients suffer from recurring acute liver inflammation (acute hepatitis). About 10% patients develop cirrhosis (scarring) of liver, leading to diminished liver functions, within early 10 years. 25% of the patients develop cirrhosis eventually. About 5% of those infected may develop liver cancer. Broadly, it may be noted that it takes one decade to develop early symptoms, about two decades to have cirrhosis, and above three decades to have cancer of the liver. Liver cancer is a fatal condition. The factors which could aggravate and influence early development of liver inflammation, cirrhosis and cancer, are: (1.) Alcohol (2.) Smoking (3.) Liver toxic drugs (4.) Exposure to chemicals (5.) Stressful life style (6.) Hepatitis B infection (7.) Hereditary tendency to cirrhosis or cancer
Females are known to have slow disease progress as compared to the male patients. Late age onset (after 40 years of age) of Hepatitis C tends to run serious course of diseases than the younger age group patients. Consumption of alcohol can increase the risk factor several folds once the diagnosis of Hepatitis C is made, as alcohol has toxic action on the liver which can aggravate the scarring (cirrhosis) of liver. Chronic sufferers after 20 to 25 years stand increased risk to develop Liver cancer, which is observed more in males, with increased risk in higher (older) age group.
#3/88/173, St. No. 5, Shaheed Jasdev Singh Nagar, opp. N.S.P School, Ludhiana, Punjab - 141116
+91 - 99154 - 14514
akalhomoeocarecentre@gmail.com